The TRS80 Model 100 portable
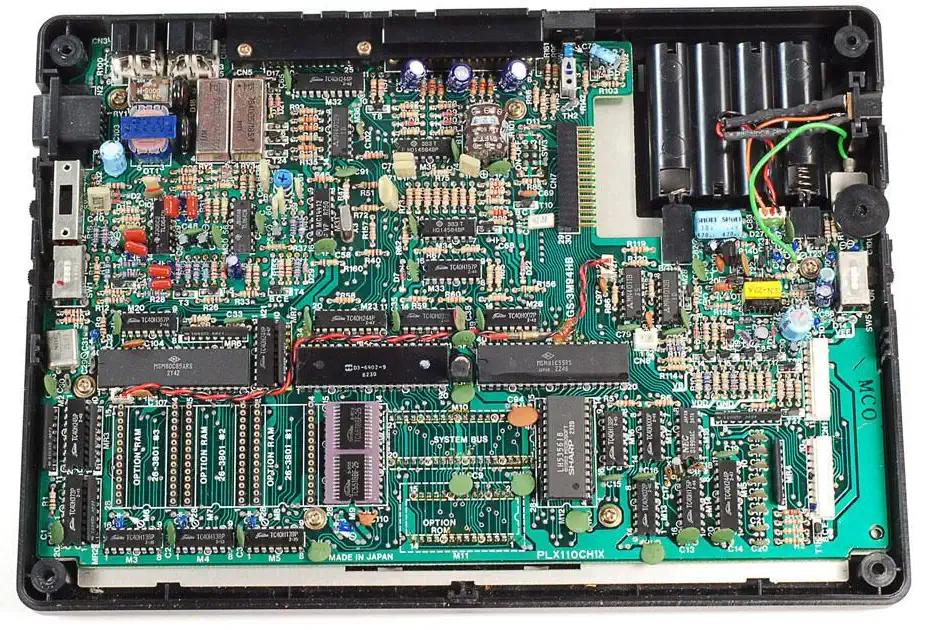
The TRS-80 Model 100 is a portable computer introduced in April 26th, 1983. It is one of the first notebook-style computers, featuring a keyboard and liquid crystal display, in a battery-powered package roughly the size and shape of a notepad or large book.
It was made by Kyocera, and originally sold in Japan as the Kyotronic 85. Although a slow seller for Kyocera, the rights to the machine were purchased by Tandy Corporation. The computer was sold through Radio Shack stores in the United States and Canada and affiliated dealers in other countries. It became one of the company's most popular models, with over 6 million units sold worldwide. The Olivetti M-10 and the NEC PC-8201 and PC-8300 were also built on the same Kyocera platform, with some design and hardware differences. It was originally marketed as a Micro Executive Work Station (MEWS), although the term did not catch on and was eventually dropped.
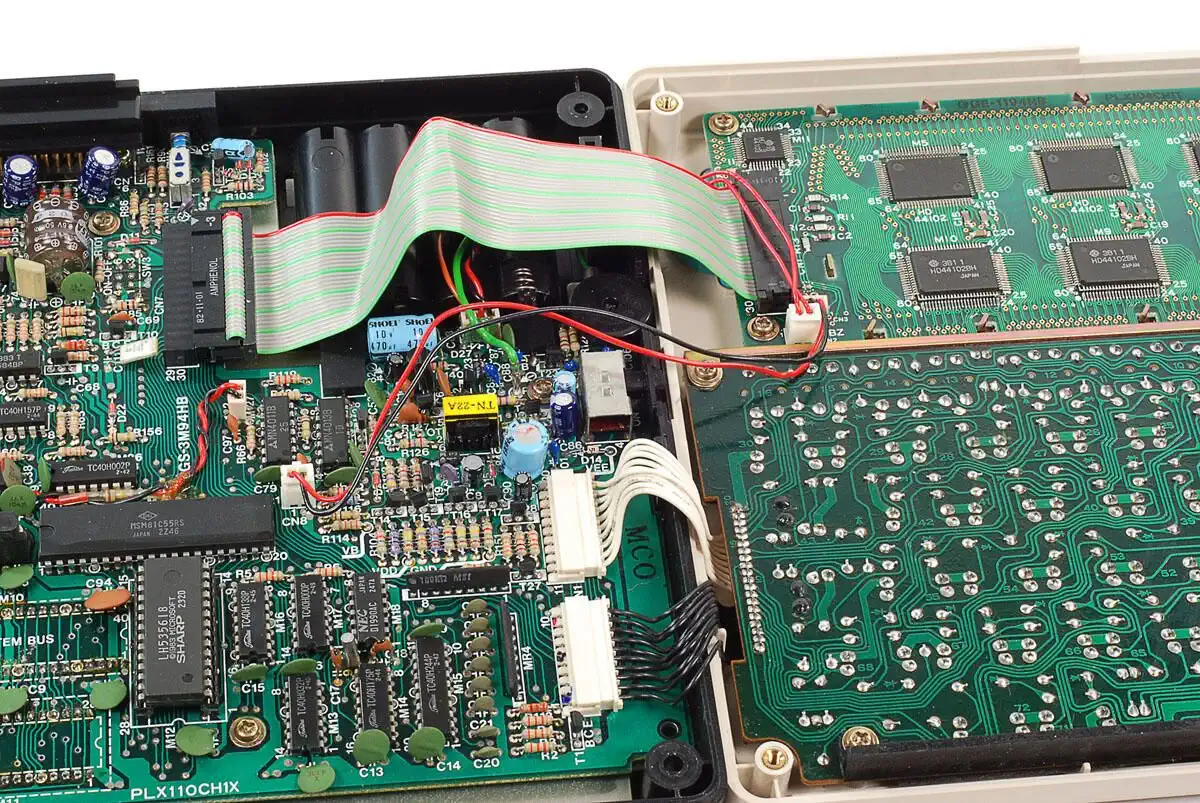

HD44100 LCD Column Driver Chip
Key features and details of the HD44100 series (which includes HD44100, HD44102, and others):
LCD Column Driver The HD44100 series chips are designed to drive the columns of a dot matrix LCD display. In dot matrix LCDs, individual pixels are addressed using row and column coordinates.
Dot Matrix Displays These chips were used in small dot matrix displays, often found in pocket calculators, digital watches, and other portable electronic devices.
Controller and Driver The HD44100 series chips integrate both the controller and the driver circuitry required to interface with the LCD display.
Low Power As these chips were intended for use in battery-operated devices, they were designed to be low-power to conserve energy and extend battery life.
Limited Resolution The resolution supported by these chips was relatively low compared to modern displays. Typical displays using HD44100 series drivers might have resolutions on the order of 32x64 or similar.
Parallel Interface The chips used a parallel bus interface to communicate with the main microcontroller or system.
Intel 8085 CPU
The Intel 8085 microprocessor is produced by Intel in 1976. It is software-binary compatible with the Intel 8080, with two instructions added to support the newly added interrupt and serial I/O features.
The CPU requires less support circuitry, allowing foa a simpler and less expensive production process. The "5" in the 8085 signifies the single +5 volt power supply that is needed to power the CPU. In comparison the 8080 needed +5V, -5V and +12V in order to run.
The 8085 uses a multiplexed address/data bus (AD0 through AD7). Intel introduced several support chips with this address latch built in, such as the 8155 RAM chip, and I/O chips. This architecture reduced the number of traces between the 8085 and supporting memory and I/O chips.
The Zilog Z80 eclipsed both the 8080 and the 8085 in capabilities and added instructions. But thanks to the built-in serial I/O and five prioritized interrupts, the Intel 8085 played a large role as a controller in many products.

RAM max: 32kB Sound Chip none Sound mono piezo beeper Display Chip Hitachi HD44102 Dot Matrix LCD Column Driver Chip Display 40x8 text mono Best Text 40x8 Best Color none Best Graphics 240x64 dot LCD Sprites n/a System OS TRS-DOS Storage External Tape drive, external disk drives Original Price $1099

