Robotron KC 85/3
The Robotron KC 85/3 was released in 1986 in East Germany. The computer was based on the Z80 CPU, had 32KByte of RAM and a 320x256 16 color graphics mode. KC stands for Klein Computer, or Micro Computer in English. The machine could be expanded by various modules: Assembly language Module, a Forth module, Digital I/O module, RAM expansion, A/D converters and more. The number of expansion slots could be increased by adding a 4-bay expansion module.
They keyboard of the KC 85 was problematic, the keys were not the full-stroke style, and the keyboard was controlled by the U807D chip, an Eastern European clone of the SAB3021. This chip was designed for remote controllers, but the two-line serial connection was prone to interference, causing ghost key inputs.
There was no text modus available on the KC, instead there was an emulated text mode in graphics, which was very slow, causing the whole system to be sluggish.



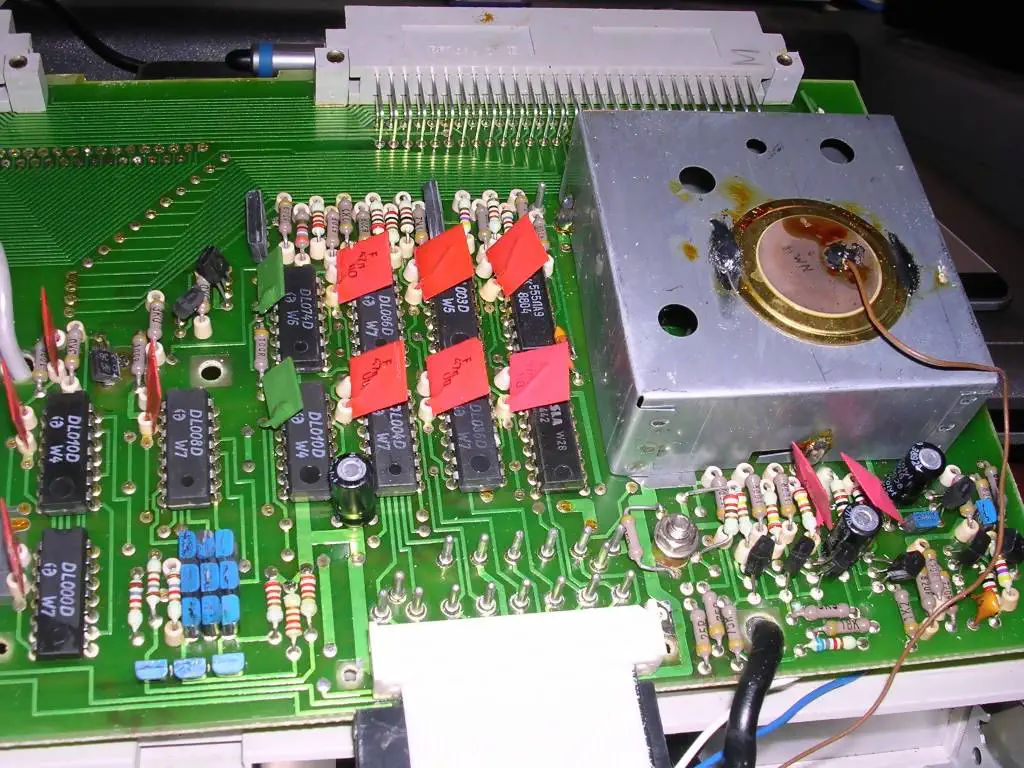
Zilog Z80 CPU Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000. The design was licensed to Synertek and Mostek as well as the European SGS.
The Z80s instruction set is binary compatible with the Intel 8080, so that 8080 code such as the CP/M Operating System and Intel's PL/M compiler for the 8080 can run unmodified on the Z80. The Z80 had many enhancements over the 8080 such as 16-bit data movement instructions, block copy and block I/O instructions, single bit addressing of all registers, IX/IY offset registers, better interrupt system and a complete duplicate register file for context switching during an interrupt.
Source: WikiPedia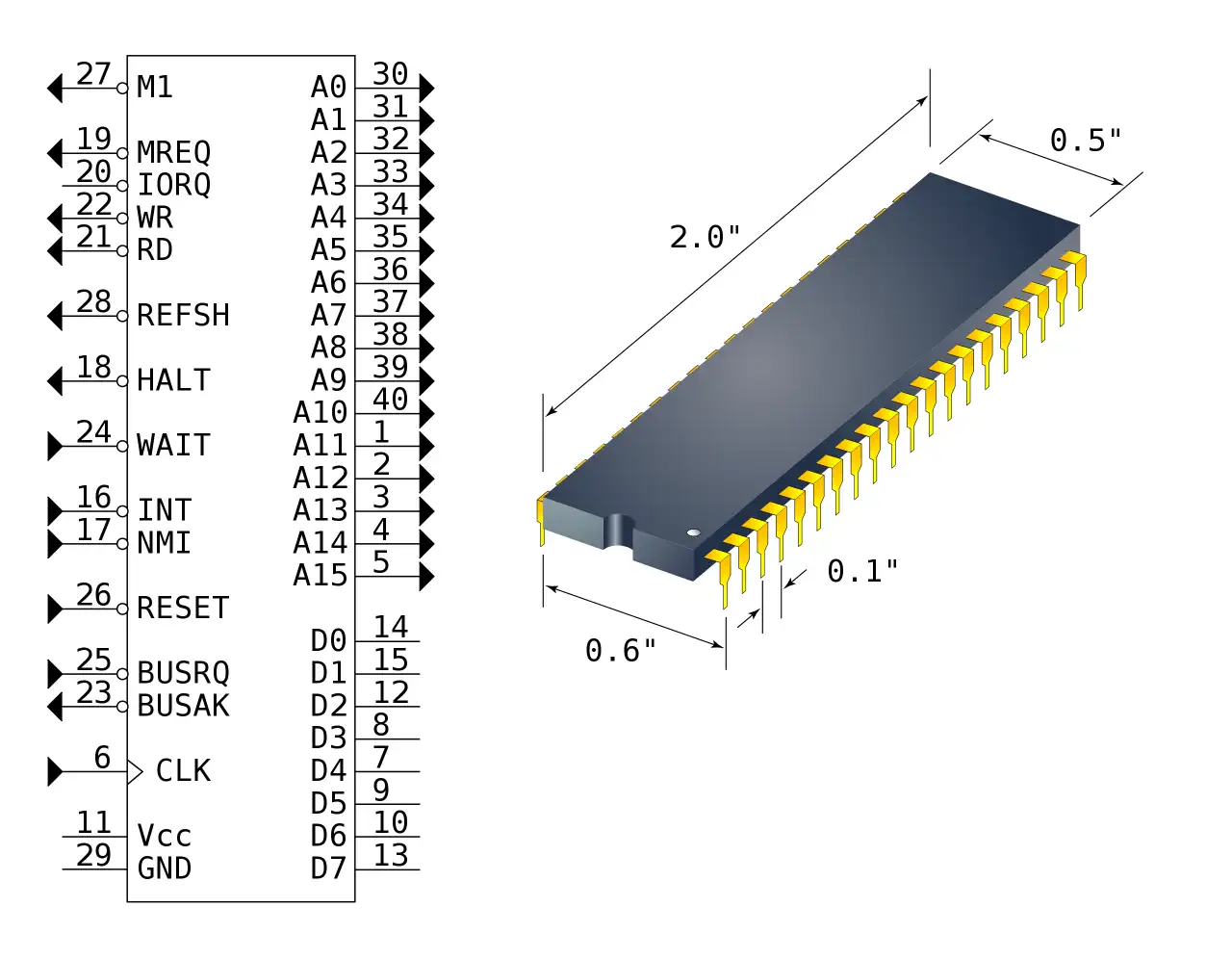
ROM: 16kB Sound Chip none Sound 2 tone generators, internal speaker Display Chip none Display 320x256 16 color, 40x32 emulated text Best Text 40x32 Best Color 16 colors Best Graphics 320x256 Sprites n/a System OS CAOS 3.1

