Amstrad PCW10 / 16
The PCW10 was basically a Amstrad PCW9256 with 512KByte of RAM, Locoscript 1.5 instead of Locoscript 1. It was not a success due to the fact that it still ran on the slow Z80 architecture, compared to the 16-bit 8086 architecture of competing MS-DOS systems.
In 1995 Amstrad released the PCW16. Despite having the same PCW branding, the system was not compatible with any of the previous PCW systems. The PCW16 came with a new GUI operating system called Rosanne. It was not capable of multi-tasking, so only one application could be run at a time. If a user started a new application, the running application would save it's files and close. The Word Processor that came with the PCW16 was created by Creative Technoloty and for backwards compatibily could read the older Locoscript files, but saved them in its own format. The sofware bundle also included a spreadsheet, address book, diary, calculator, and a file manager. No third party software was produced for this system.
The PCW16 was capable of a more standard 640x480 pixels in VGA mode. It came with a 1.4MByte High Density floppy disk drive and had 1 1MByte Flash memory to store programs and user files. The PCW16 still used the older Z80 CPU, but at higher speed than it's predecessors.

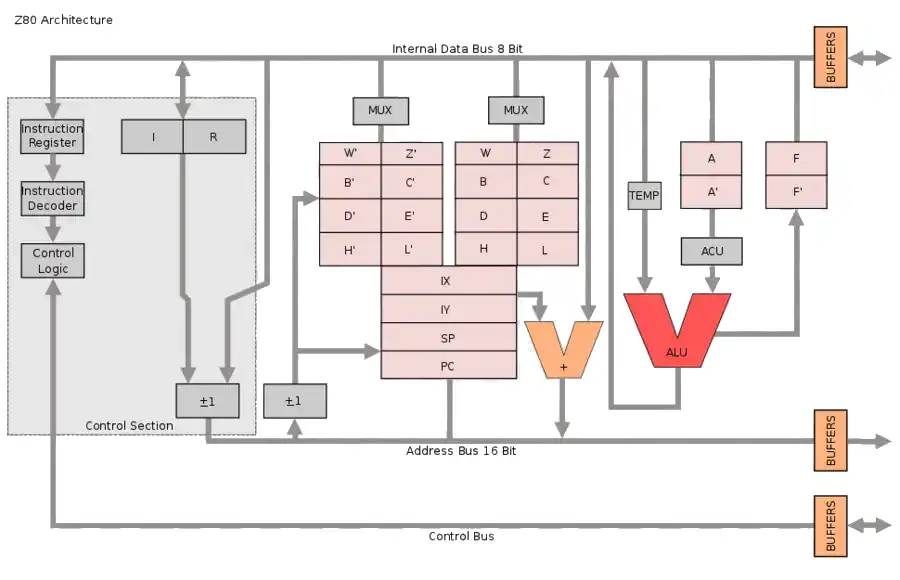
Zilog Z80 CPU Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000. The design was licensed to Synertek and Mostek as well as the European SGS.
The Z80s instruction set is binary compatible with the Intel 8080, so that 8080 code such as the CP/M Operating System and Intel's PL/M compiler for the 8080 can run unmodified on the Z80. The Z80 had many enhancements over the 8080 such as 16-bit data movement instructions, block copy and block I/O instructions, single bit addressing of all registers, IX/IY offset registers, better interrupt system and a complete duplicate register file for context switching during an interrupt.
Source: WikiPedia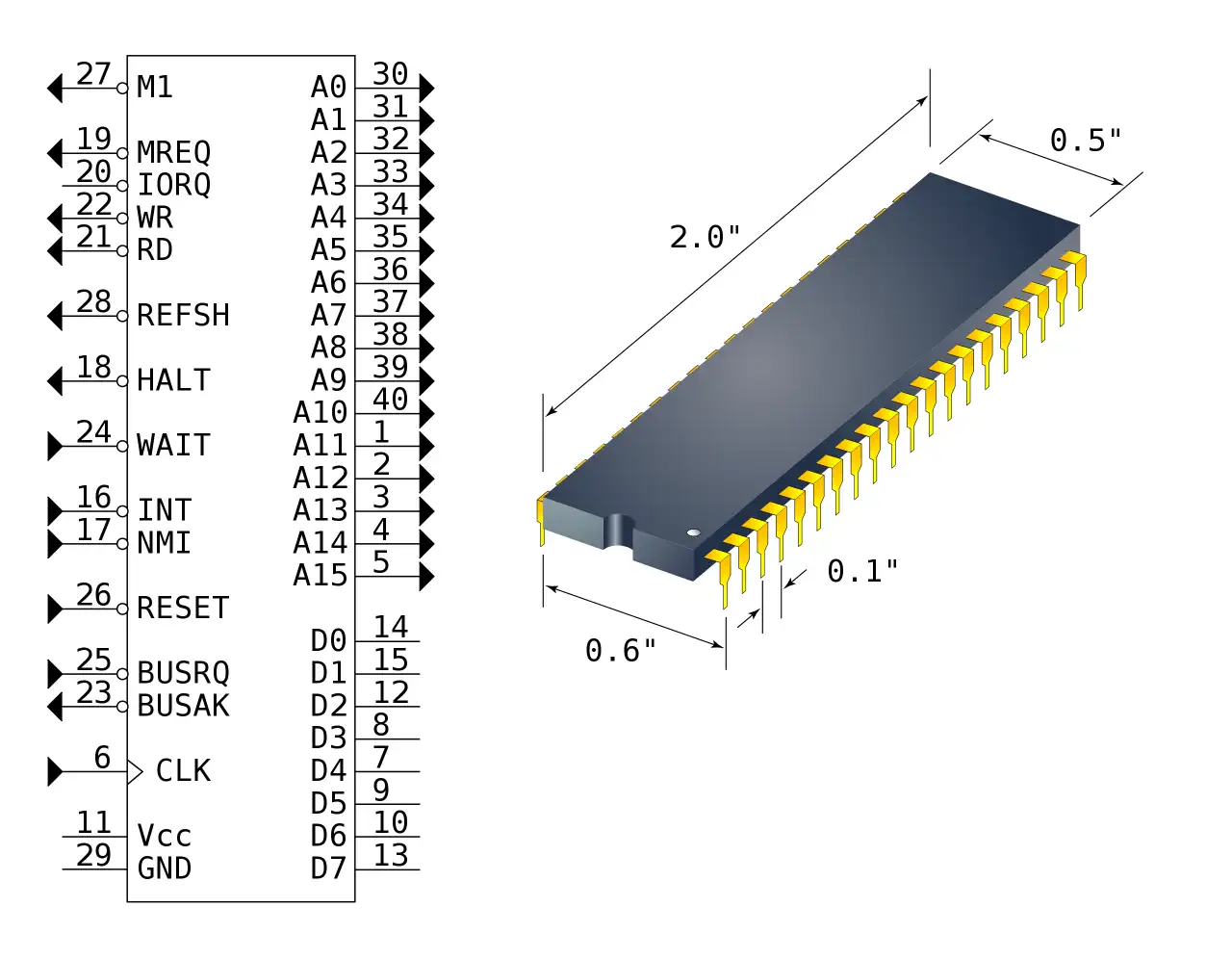
1MB Flash RAM Sound Chip none Sound 1 channel Display Chip none Display 640x480 mono Best Color monochrome Best Graphics 640x480 monochrome Sprites none System OS Rosanne GUI
CP/M Plus Storage Internal 3.5" 1.4MByte High HD Disk Drive


