Introduction
The Sharp MZ-80K was introduced in 1978 on the Japanese market in kit form. In 1979 it was introduced in Germany, but not as a kit for the price of DM 1800. In UK it was officially unveiled in October 1979 at the Birmingham International Business Show for the price of £600. Later 2 new models were available: MZ-80K2 ( Japan 1980 ) and MZ-80K2e ( Japan 1981 ) all in Japan available only.
After market kits became available to change the 40-colum display hardware for an 80-column one, so that the machine could run CP/M, which opens it to a wide range of software. The standard CPU speed of 2MHz can be easily changed to 4MHz, making the machine twice as fast.
The MZ-80K was a big success: about 100,000 systems were sold.
Sharp LH0080A CPU
The Sharp LH0080A is a microprocessor produced by Sharp, and is fully compatible with the Zilog Z80. The LH0080A has been used in various computers:
- Sharp 8-bit MZ-series (MZ-80 through MZ-800)
- Sony HB-55 MSX
- HotBit HB-8000
Zilog Z80 CPU Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000. The design was licensed to Synertek and Mostek as well as the European SGS.
The Z80s instruction set is binary compatible with the Intel 8080, so that 8080 code such as the CP/M Operating System and Intel's PL/M compiler for the 8080 can run unmodified on the Z80. The Z80 had many enhancements over the 8080 such as 16-bit data movement instructions, block copy and block I/O instructions, single bit addressing of all registers, IX/IY offset registers, better interrupt system and a complete duplicate register file for context switching during an interrupt.
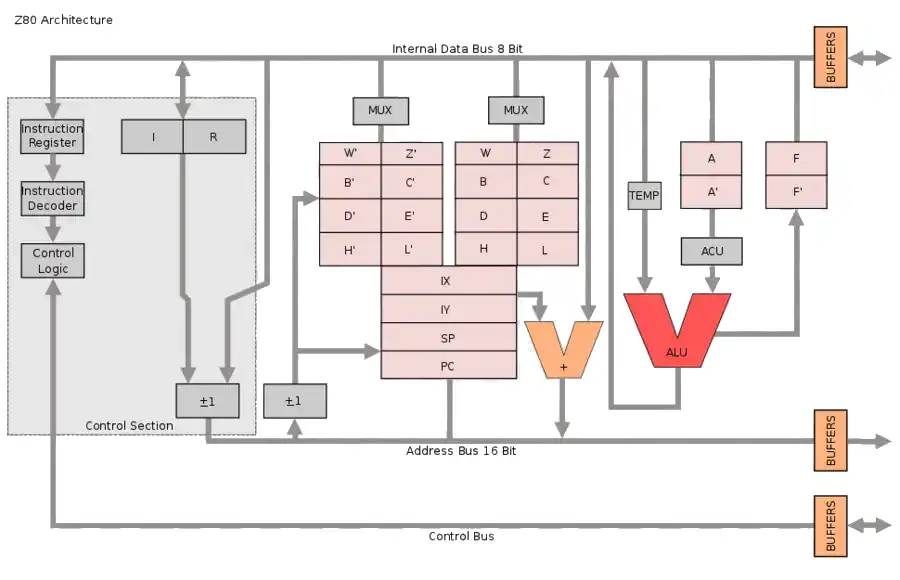
Source: WikiPedia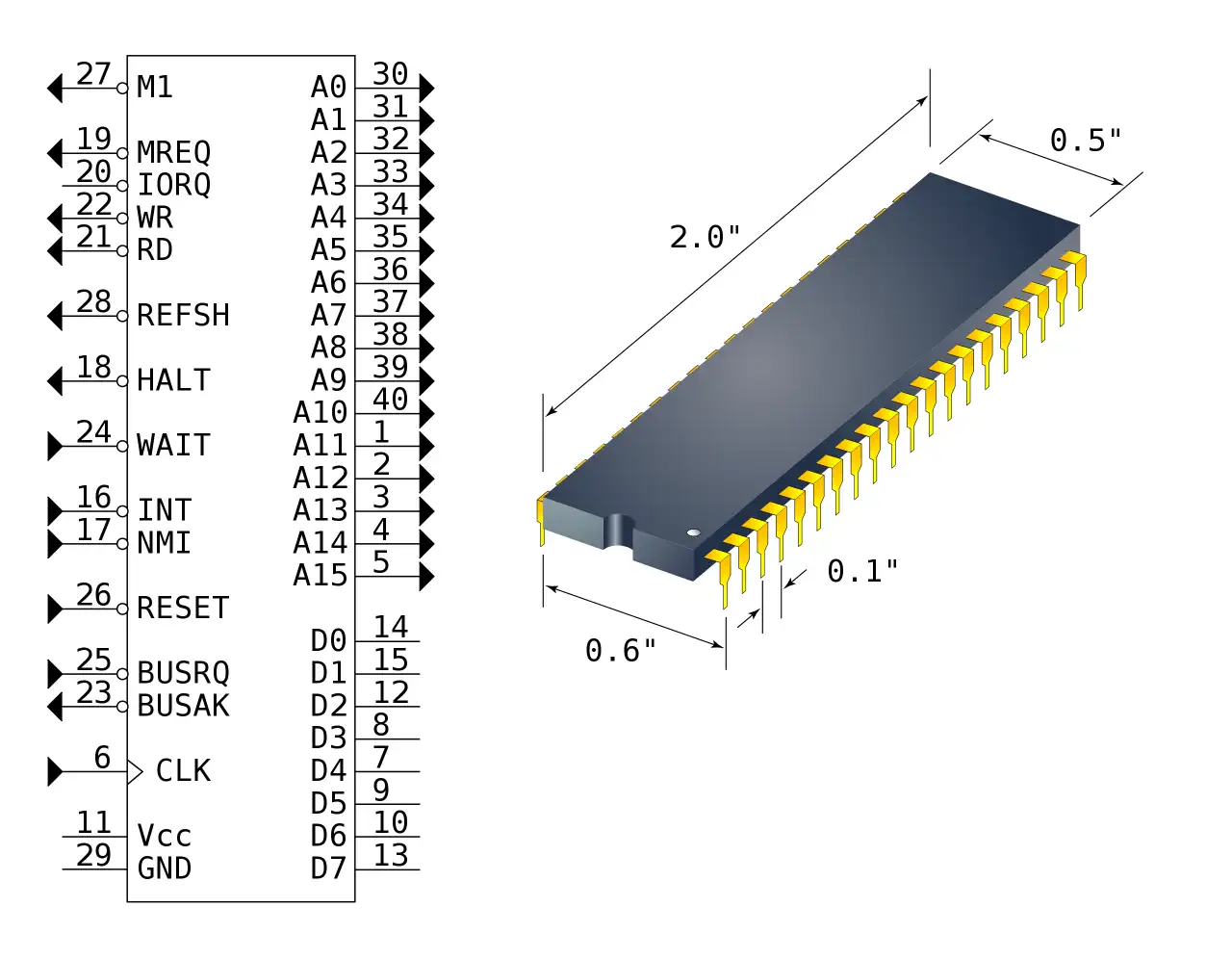
RAM max: 48kB
VRAM: 1kB Sound Chip Intel 8253 PIT generating square wave Sound 1 square wave channel. Display Chip none Display 40x24 Text only Best Text 40x24 Best Color none Best Graphics Text Only Sprites none System OS Monitor System Original Price $1800

