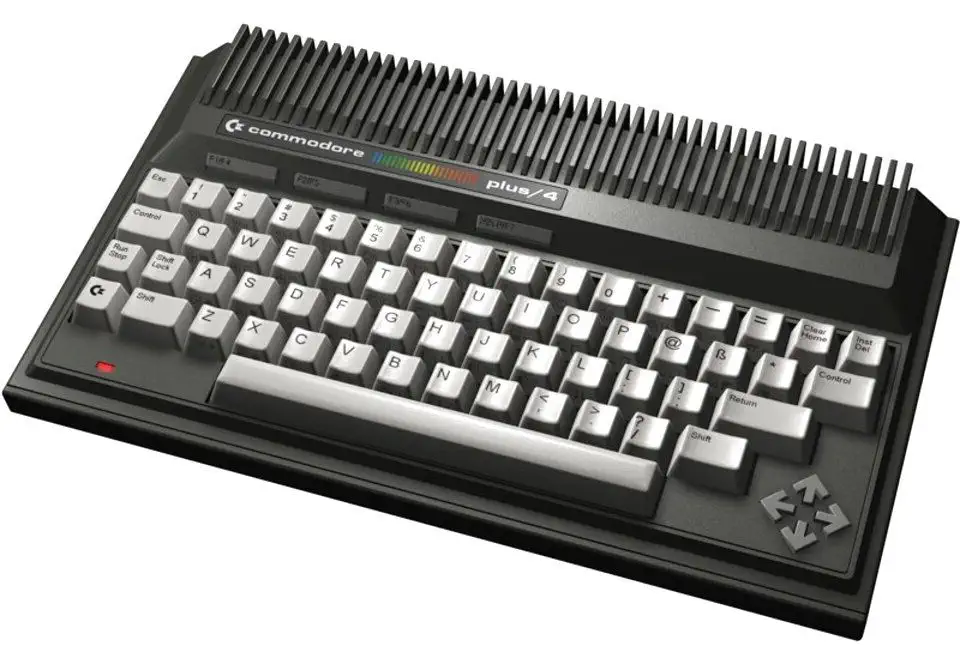
Commodore Plus/4
The commodore Plus/4 was released in 1984. The name refers to the four built in applications, a word processor, a spreadsheet, a database and a graphing program. The plus/4 was introduced as a productivity computer with the software built-in.
The machine was a complete flop in the US where it was called the "Minus/60" a pun on the difference with the successful commodore 64. The idea of the computer was to provide Commodore with a cheap alternative to machines of the competition, such as the Timex Sinclar range. Jack Tramiel wanted a slice of the budget computer market as he was convinced that Japanese companies where about to overtake the American home computer market, as this had happened with the audio and video markets.
The machine is internally much like the Commodore C16 and the C116, it is also built around the 8501 CPU and the TED video/sound chip. The Plus/4 had 64KByte of memory but the price point made it a direct competitor of Commodore's own C64. Existing peripheral devices, such as the 1531 datasette, or the 1551 disk drive were all incompatible, adding to the failure of the Plus/4.
Source C64 WikiCommodore Plus/4 Block Diagram

Commodore Basic 3.5 boot screen

Packaging variations


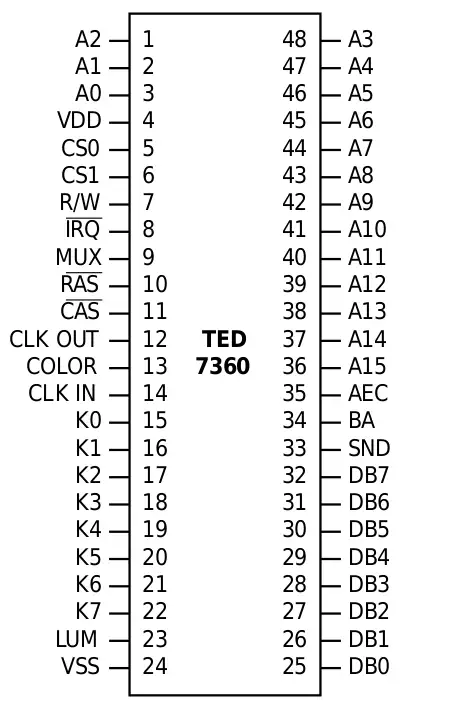
TED - Text Editing Device
The 7360 Text Editing Device or TED, was an integrated circuit made by MOS Technology Inc. It was a video chip that also contained sound generation hardware, DRAM refresh circuitry, interval timers, and keyboard input handling. It was specifically designed for the Commodore Plus/4 and the Commodore 16.
The video capabilities provided by TED were basically a subset of those in the VIC-II chip. The TED supports five video modes:
- 40x25 Text Mode, 8x8 pixel characters
- Multicolor text (4x8 pixels per character, double pixel width)
- Extended background color mode (8x8 pixels per character)
- 160x200 Multicolor Graphics
- 320x200 Hi-Res graphics
MOS 7501/8501 CPU
The MOS 7501 and 8501 was introduced in 1984 and both chips are a variant of the 6510. Where the 6510 had 6 I/O ports, the 7501 and 8501 used all 8. However the CPU omits the pins for the non-maskable interrupt and the clock output. The 7501/8501 were used in the commodore 16, the commodore 116 and the Commodore Plus/4 computers. The I/O ports controlled the Datasette and the CBM Bus interface.
The 7501 and 8501 were functionally equivalent, but the manufacturing process was different. The 7501 was manufactured with HMOS-1, and the 8501 was manufactured with HMOS-2. HMOS-2 used a channel length of 2 microns against the 3 microns of HMOS-1.
Source: WikiPedia

ROM: 64kB Sound Chip TED 7360 Sound 2-channel, 4-octave + white noise Display Chip TED Display 320x200 121 colors (15 colors, 8 luminances) Best Color 121 colors Best Graphics 320x200 in 121 colors Sprites none System OS Commodore BASIC 3.5 Original Price $299

