The Commodore 128 dual CPU computer
The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128, is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). It was introduced in January 1985 at the CES in Las Vegas, and appeared three years after its predecessor, the Commodore 64.
The C128 is a significantly expanded successor to the C64, with nearly full compatibility. The newer machine has 128 KB of RAM in two 64 KB banks, and an 80-column color video output. It has a redesigned case and keyboard. Also included is a Zilog Z80 CPU which allows the C128 to run CP/M, as an alternative to the usual Commodore BASIC environment. The presence of the Z80 and the huge CP/M software library it brings, coupled with the C64's software library, gave the C128 one of the broadest ranges of available software among its competitors. The primary hardware designer of the C128 was Bil Herd, who had worked on the Plus/4.
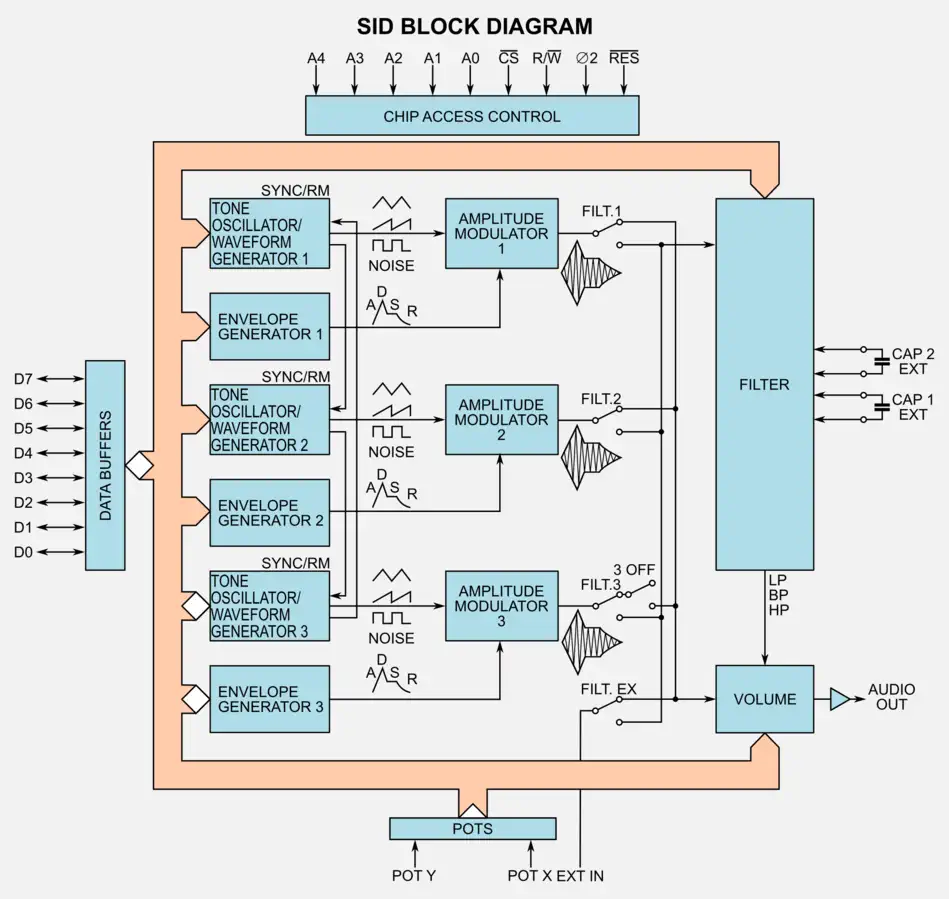
SID (MOS 6581) - Sound Interface Device
SID is short for Sound Interface Device. It is the name of the sound chip that was used in the VC10, the commodore 64 and the Commodore 128. SID was developed by Bob Yannes, an employee of MOS Technology. Bob was not only an engineer but also knew a lot about music. His intention was to create a different sound chip than other devices at the time. He implemented a subtractive synthesis chip. The chip's distinctive sound is easily recognized and was clearly ahead of the ocmpitition. The SID combines analog and digital circuitry that cannot be 100% emulated, even today.
Source: C64 Wiki
MOS Technology VIC-II
The VIC-II, or Video Interface Chip II, is a chip from MOS Technology. There are a few variants:
- For NTSC: 6567/8562/8564
- For PAL: 6569/8565/8566
The VIC-II generates Y/C signals and DRAM refresh signals for the Commodore 64, Commodore MAX, and Commodore 128 computers. It is the successor of the original VIC chip used in the VIC-20 computer.
Features:
- 16 KByte address space for screen, character and sprite memory
- 320x200 graphics in 16 colors
- 40x25 Text resolution
- Capable of 8 sprites per scanline (24x21 or 12x21 multicolor sprites)
- Raster interrupt
- Smooth Scrolling
- Independent DRAM refresh
- BUS mastering for the 6502-style bus. CPU and VIC-II can access the bus during alternating half-clock cycles.
Programmers quickly learned that the VIC-II was more capable than the specifications would indicate. By manupulating the 47 different control registers, and by using machine code hooked into the raster interrupt routine (or the scanline interrupt), the chip can be programmed to do sprite multiplexing. This allows for more than 8 concurrent sprites on screen. It basically allows for the screen to be split up in different slices, giving each slice its own scrolling, resolution, color and sprite properties. This even allowed programmers to use graphics outside the upper and lower borders of the screen.

MOS 8502 CPU
The MOS Technology 8502 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by MOS Technology and used in the Commodore 128 (C128). It is an improved version of the MOS 6510 used in the Commodore 64 (C64). It was manufactured using the HMOS process, allowing it to have higher transistor density, and lower cost, while dissipating less heat. The 8502 allows the C128 to run at double the clock rate of the C64 with some limitations.


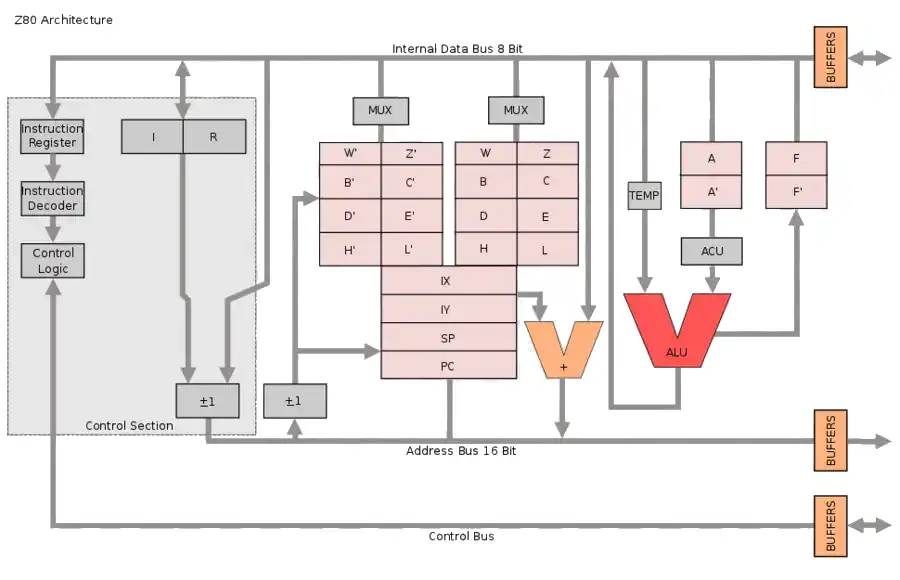
Zilog Z80 CPU Family
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000.
The Z80 microprocessor was developed by Zilog, a company founded by Federico Faggin in 1974. The Z80 was released in July 1976, as a successor to the Intel 8080. It was designed to be fully compatible with the 8080, but also included new features such as an improved instruction set, more powerful interrupts, and a more sophisticated memory management system.
The Z80 quickly became popular in the personal computer market, with many early personal computers, such as the TRS-80 and Sinclair ZX80, using the Z80 as their central processing unit (CPU). It was also widely used in home computers, such as the MSX range, SORD, and the Amstrad CPC, as well as in many arcade games. Additionally, it was also used in other applications such as industrial control systems, and embedded systems. The Z80 was widely used until the mid-1980s, when it was gradually replaced by newer microprocessors such as the Intel 80286 and the Motorola 68000. The design was licensed to Synertek and Mostek as well as the European SGS.
The Z80s instruction set is binary compatible with the Intel 8080, so that 8080 code such as the CP/M Operating System and Intel's PL/M compiler for the 8080 can run unmodified on the Z80. The Z80 had many enhancements over the 8080 such as 16-bit data movement instructions, block copy and block I/O instructions, single bit addressing of all registers, IX/IY offset registers, better interrupt system and a complete duplicate register file for context switching during an interrupt.
Source: WikiPedia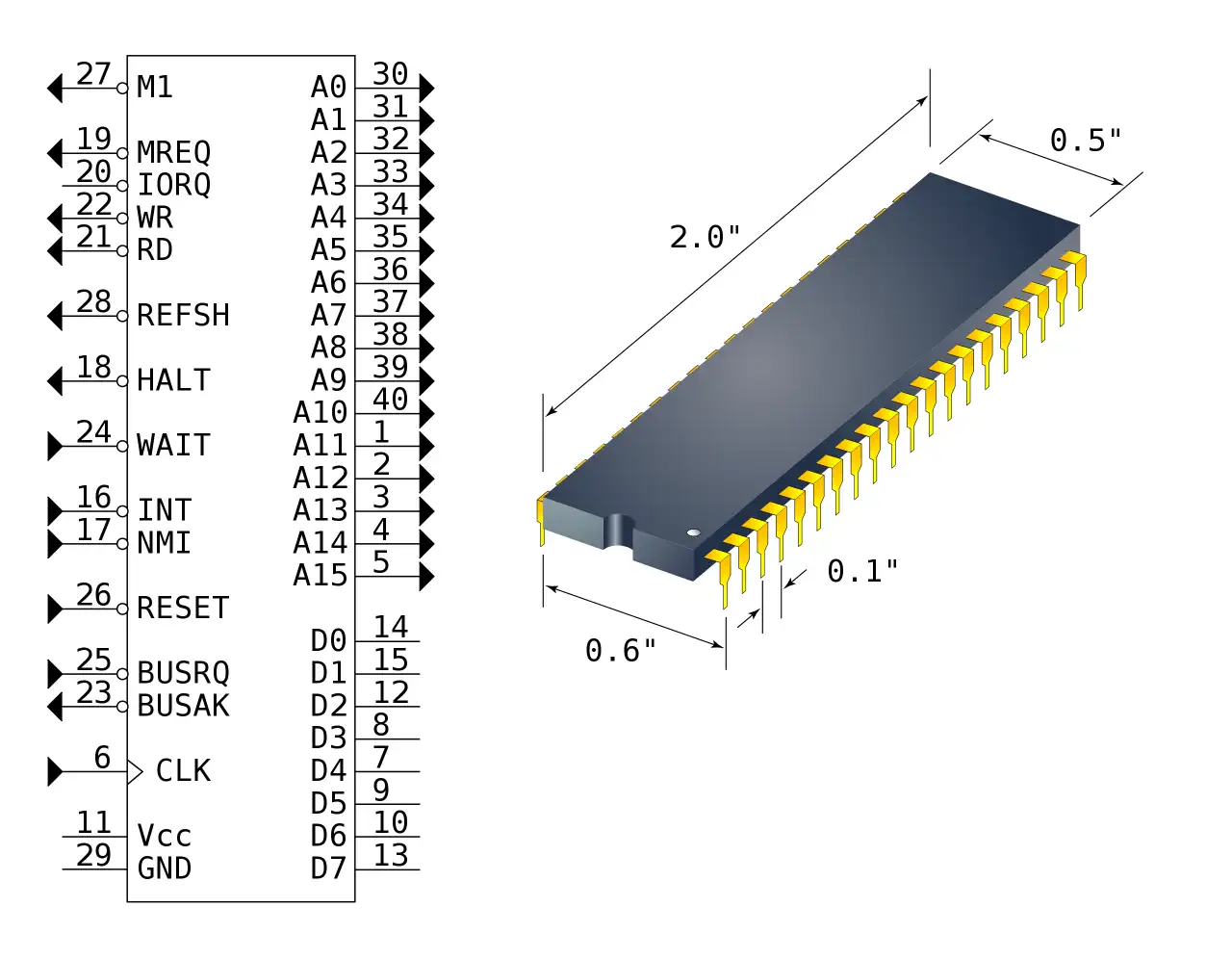
VRAM: 16kB Sound Chip SID (MOS 6581) Sound 3 osc, 4 wave channels, filters and ADSR Display Chip VIC-IIE (MOS 8564) for C64 compatibility Display 80x25 80x50 text
320x200 graphics, 640x200 graphics
640x400 interlaced graphics Best Text 80x25 Best Color 16 colors Best Graphics 640x400 interlaced Sprites 16 pixel wide, 8 per scanline, 3 colors in c64 mode System OS Commodore BASIC 7.0
CP/M Storage External Floppy Disk Drive

